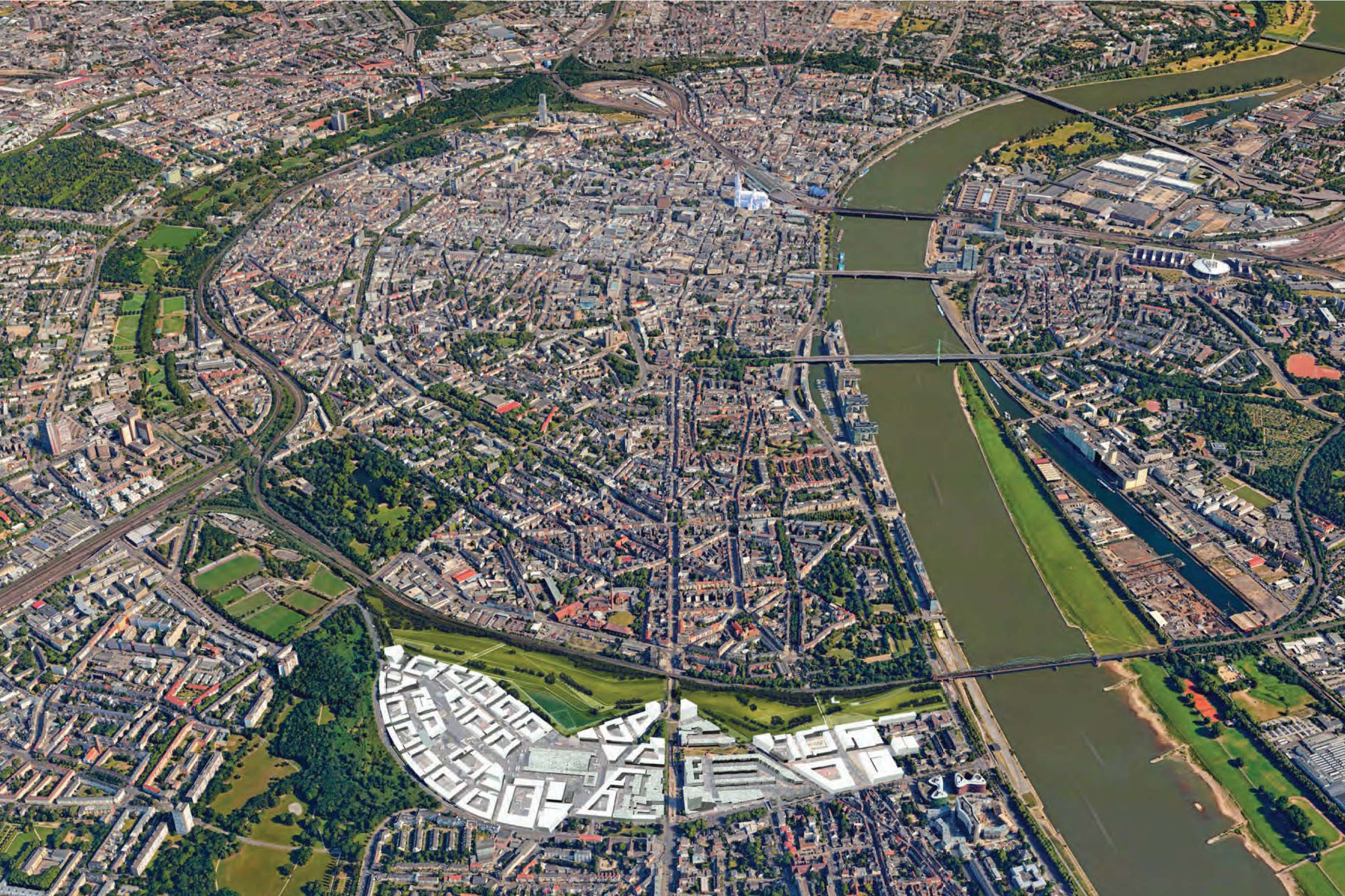
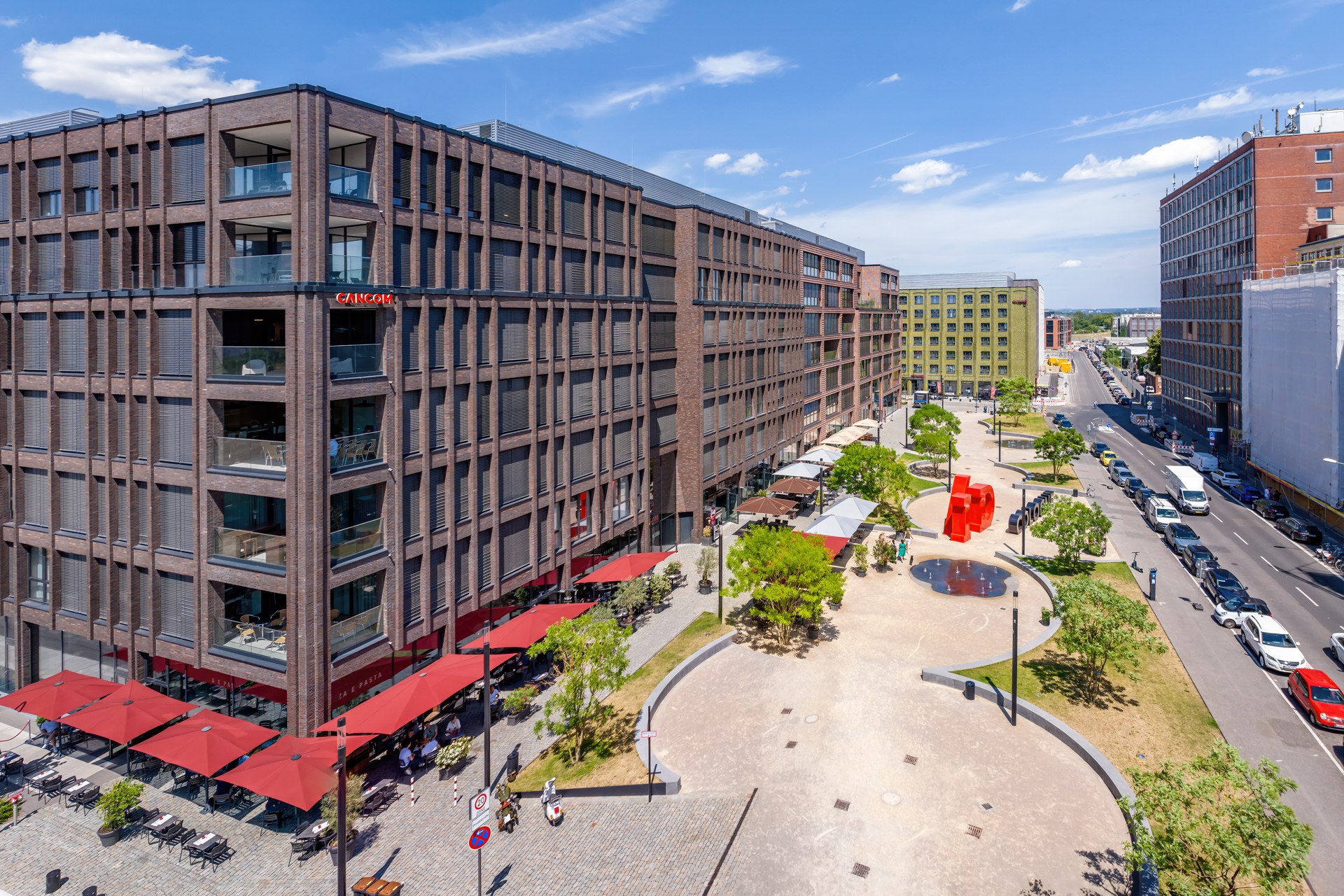
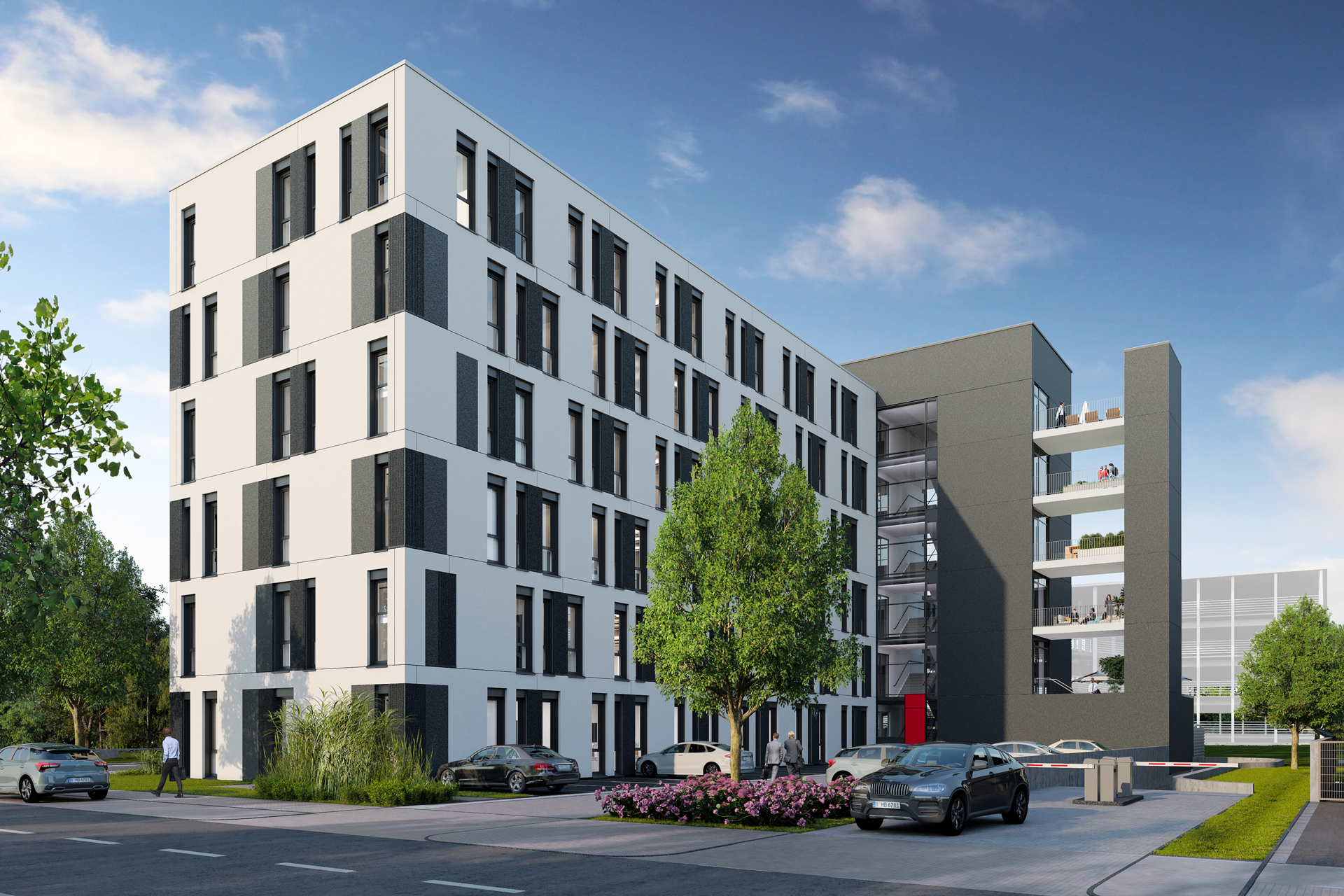
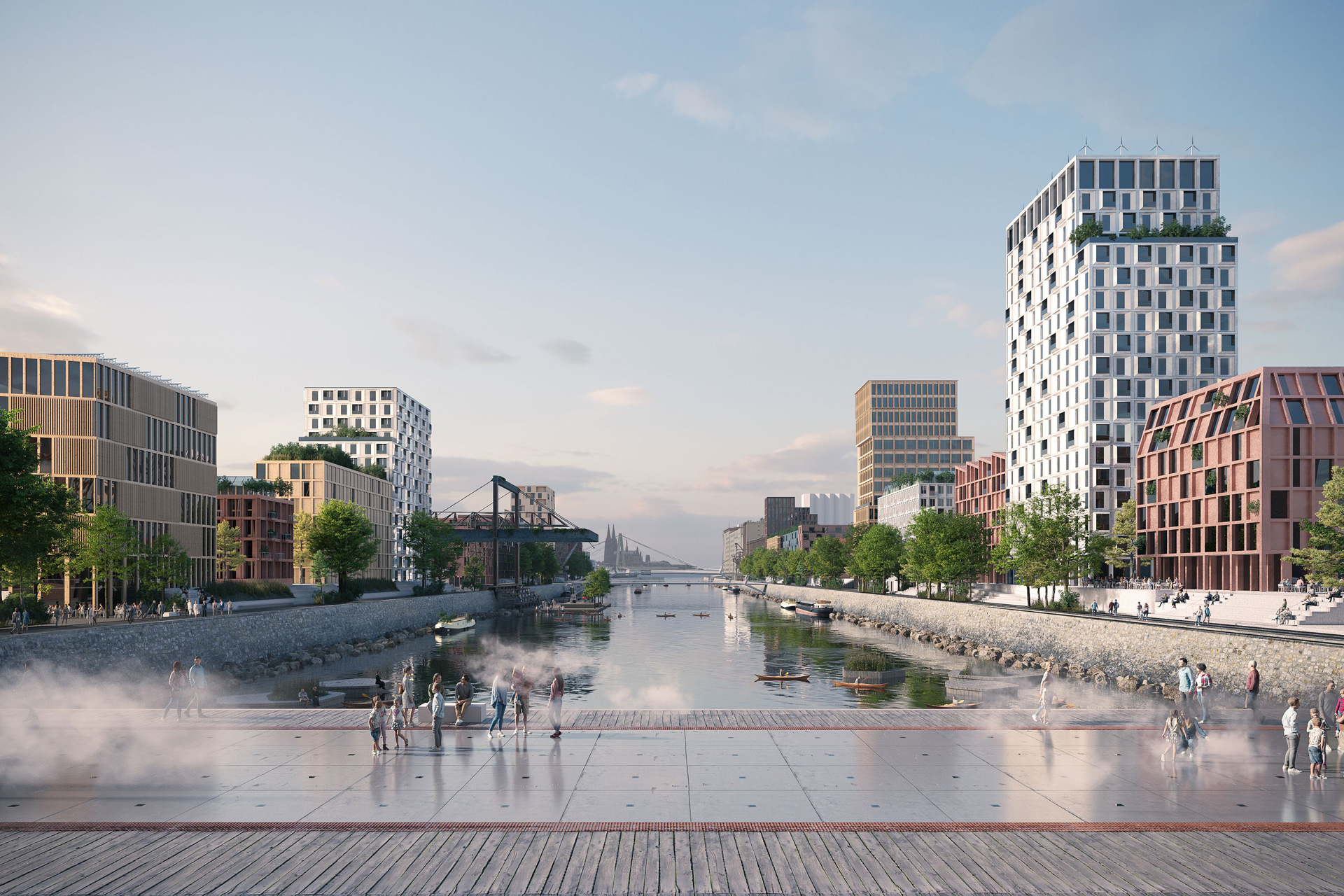
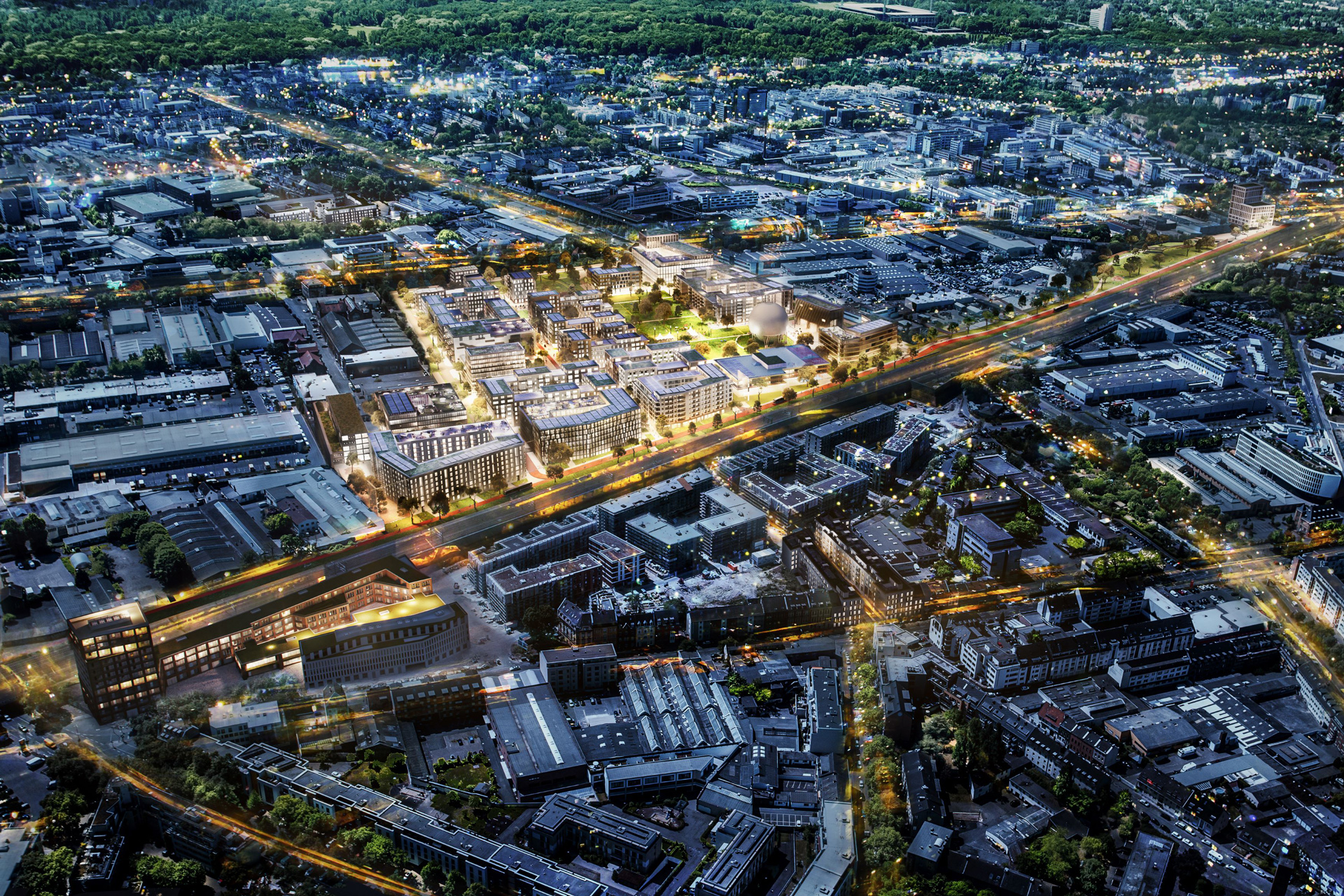
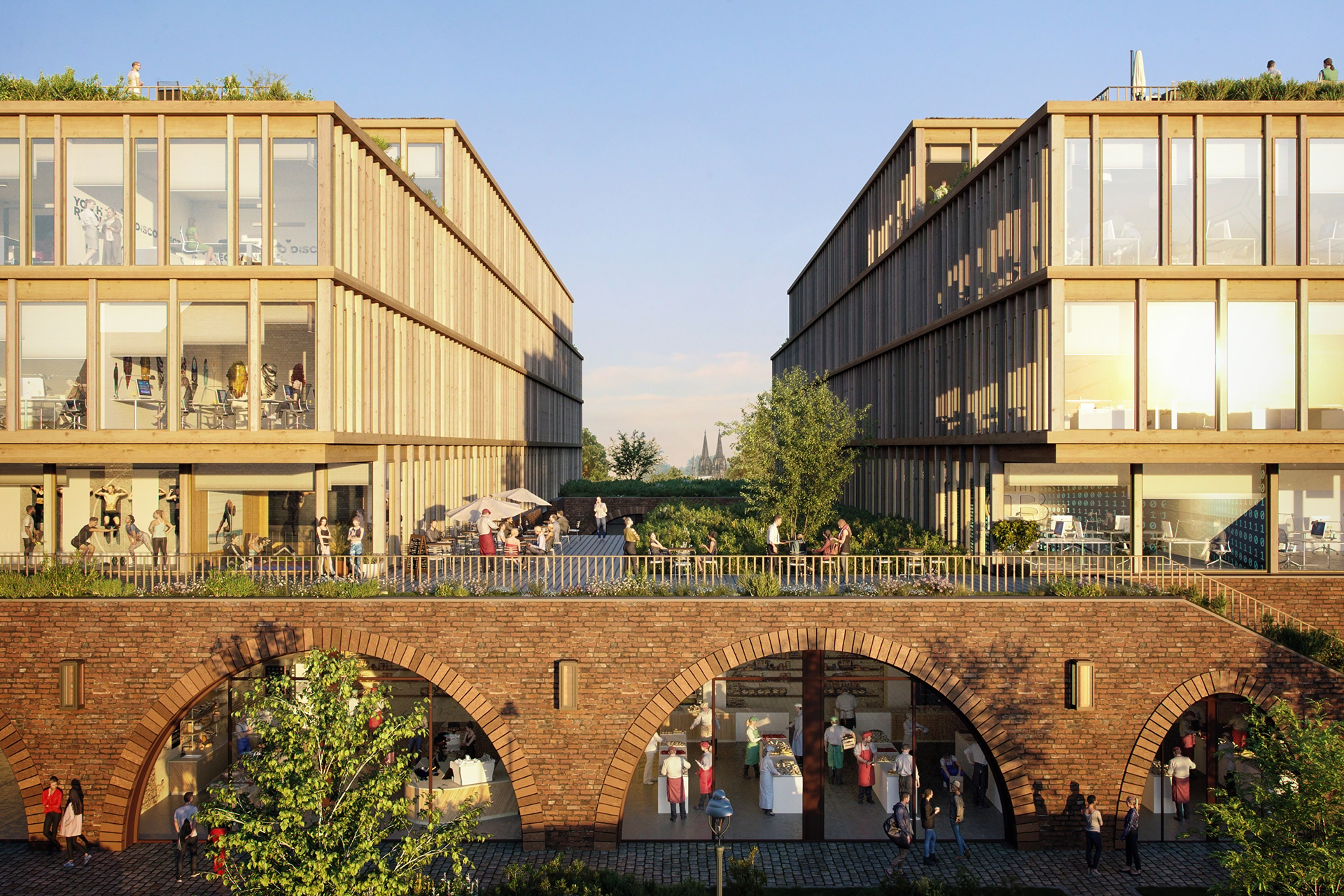
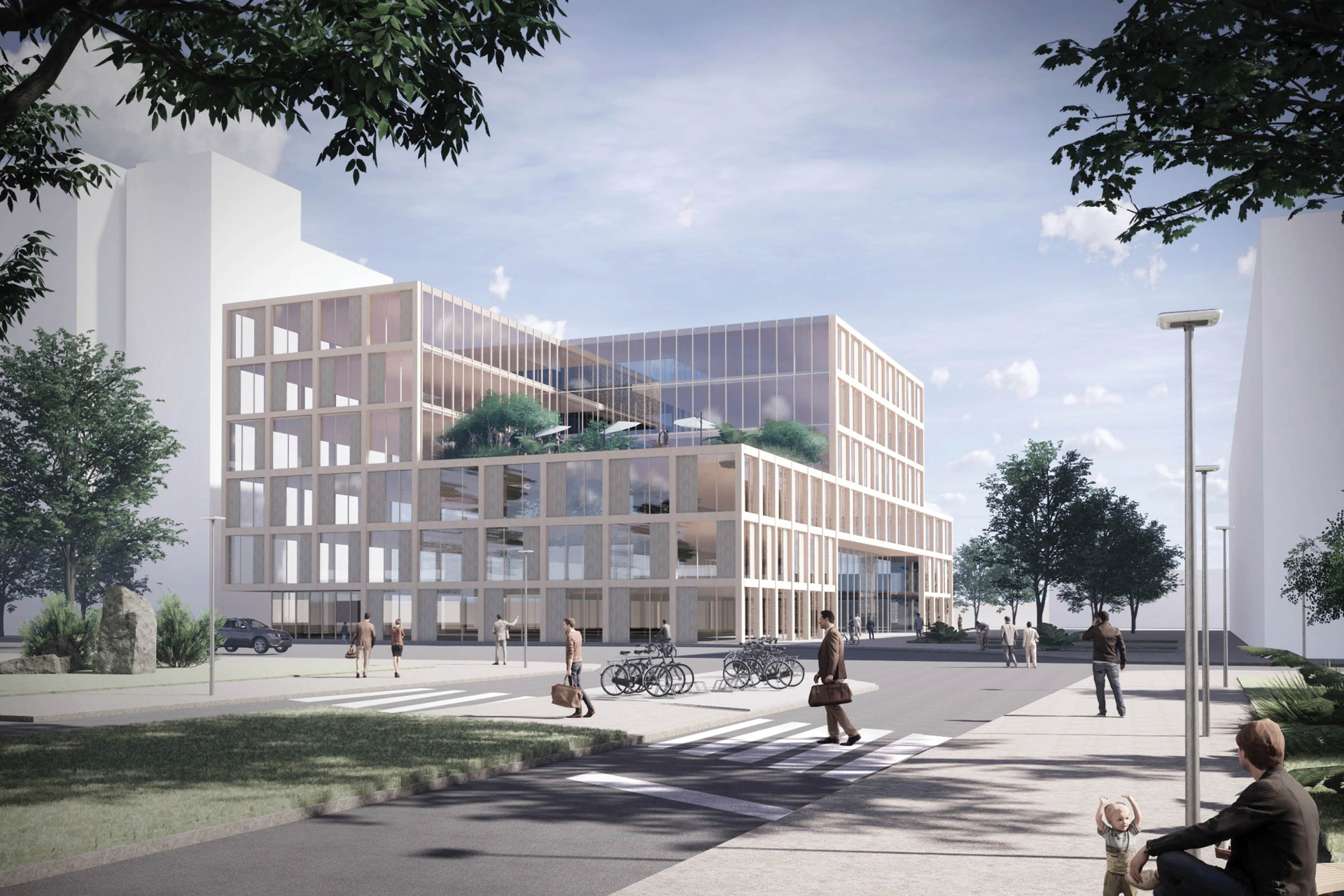
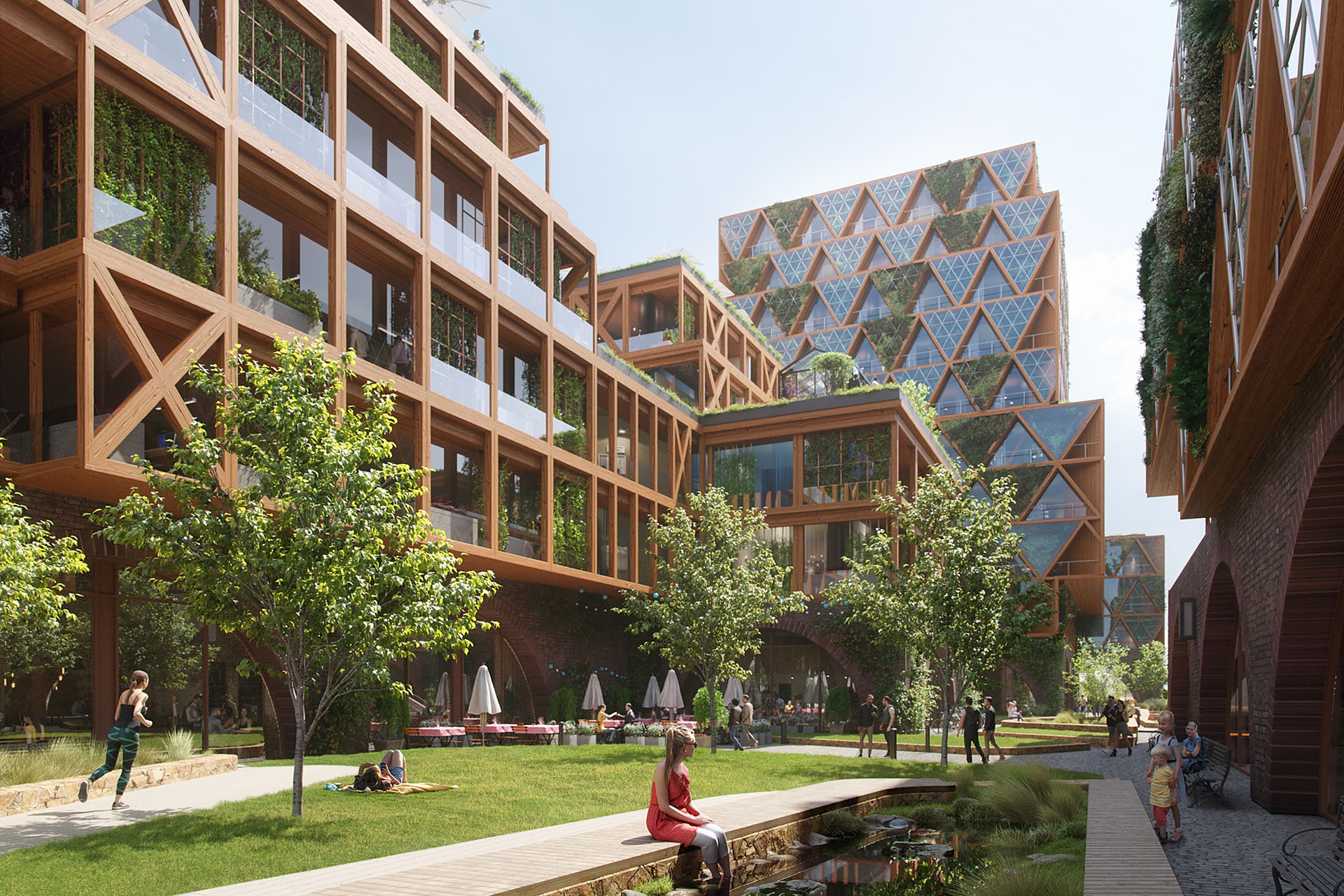
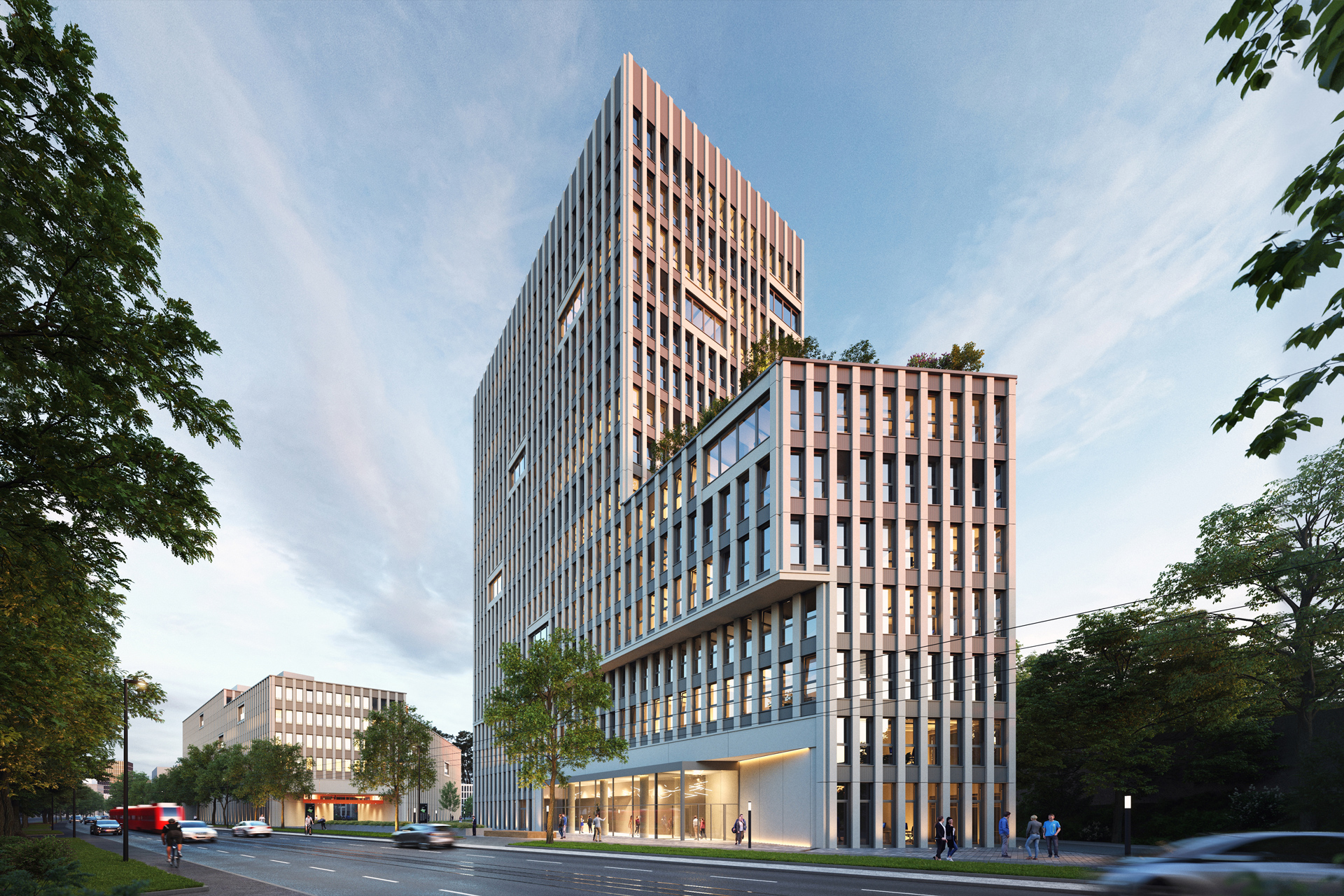
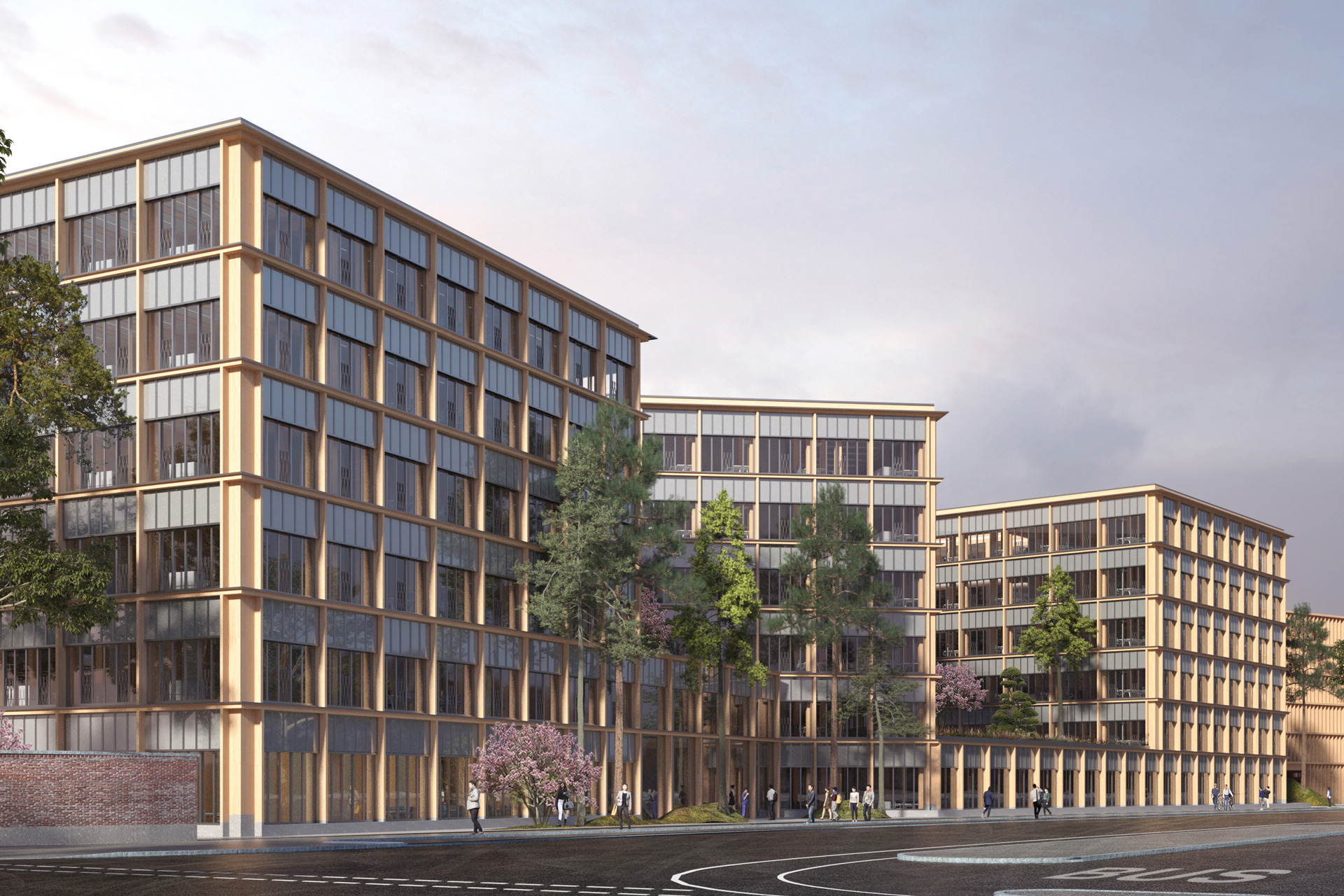
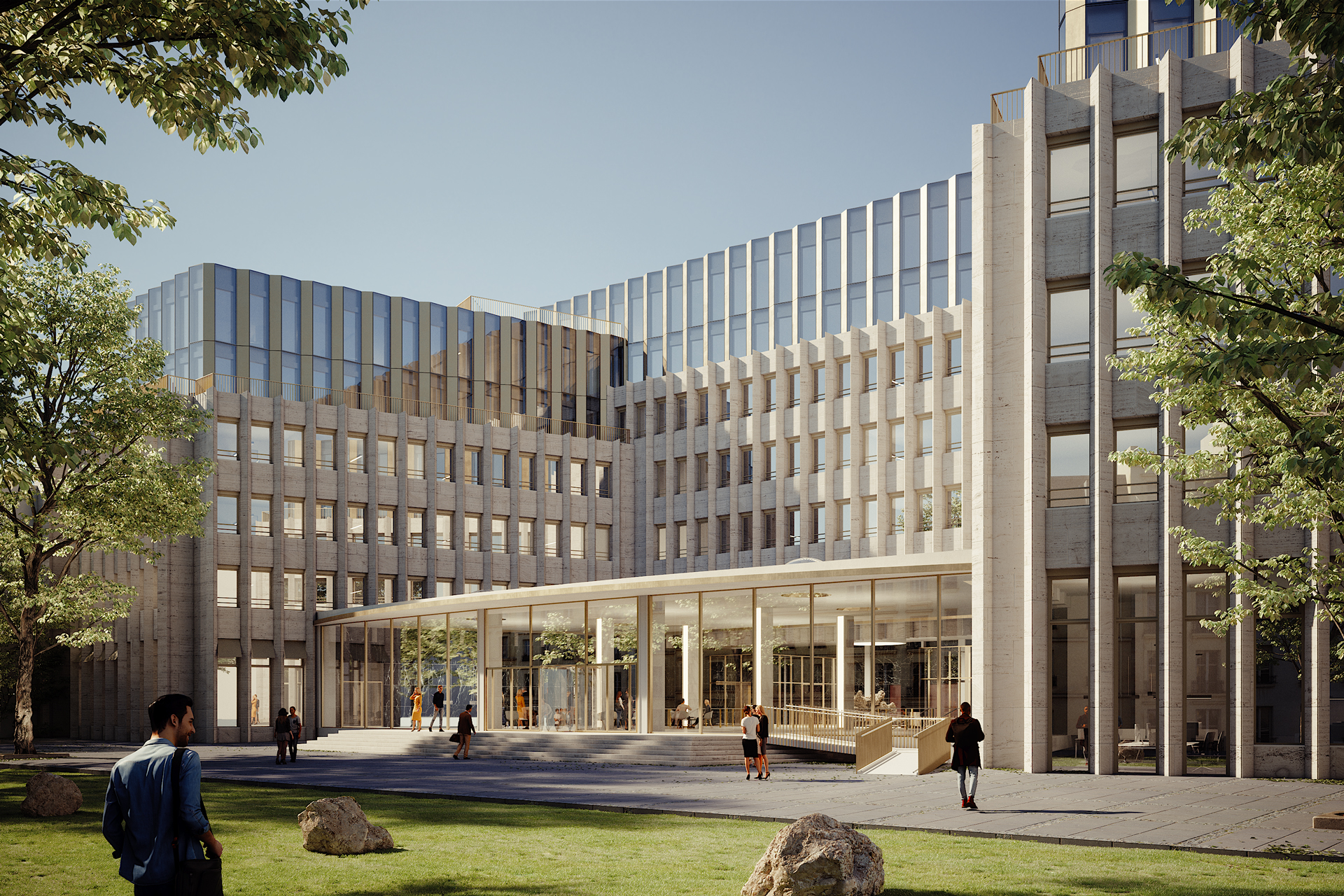
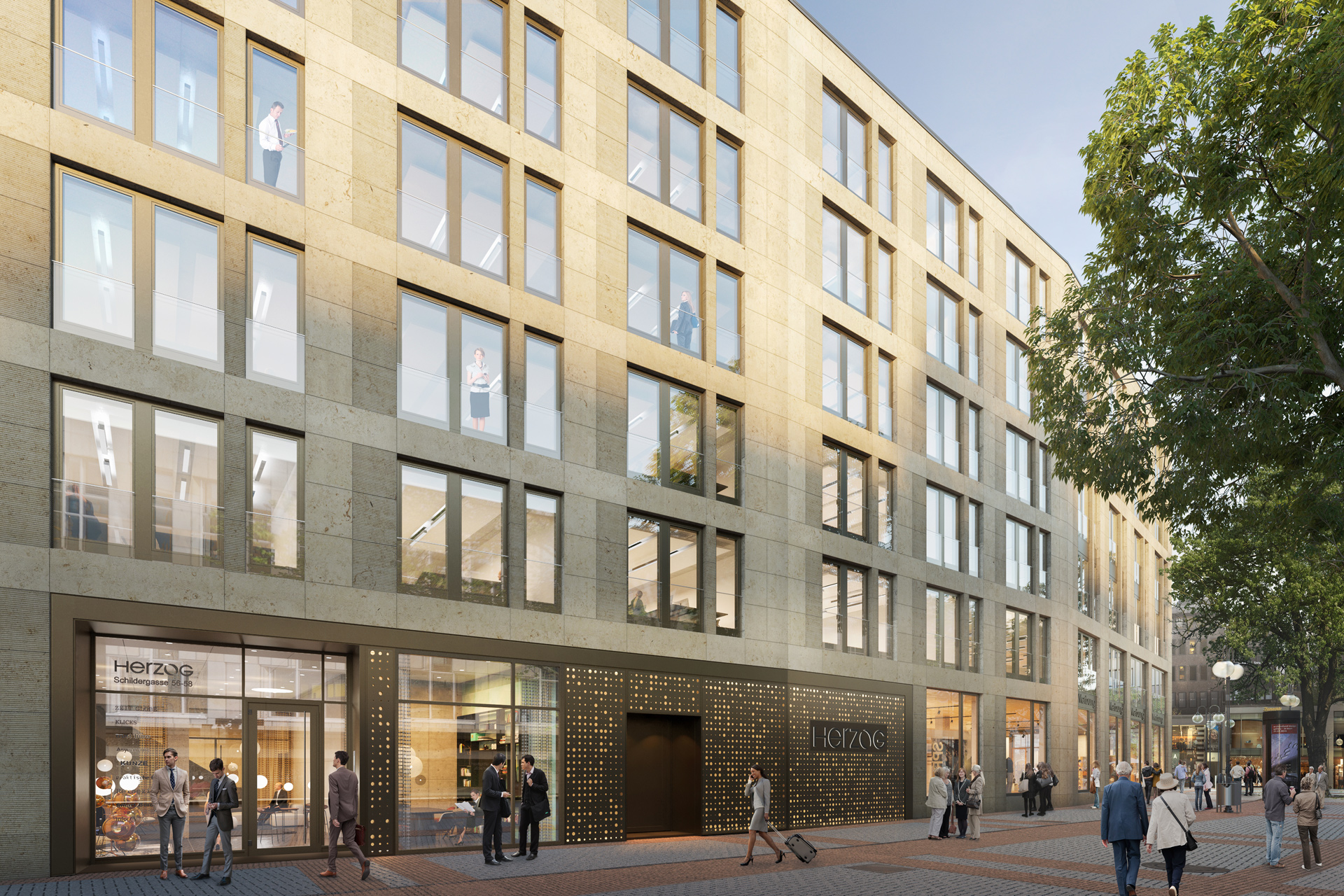
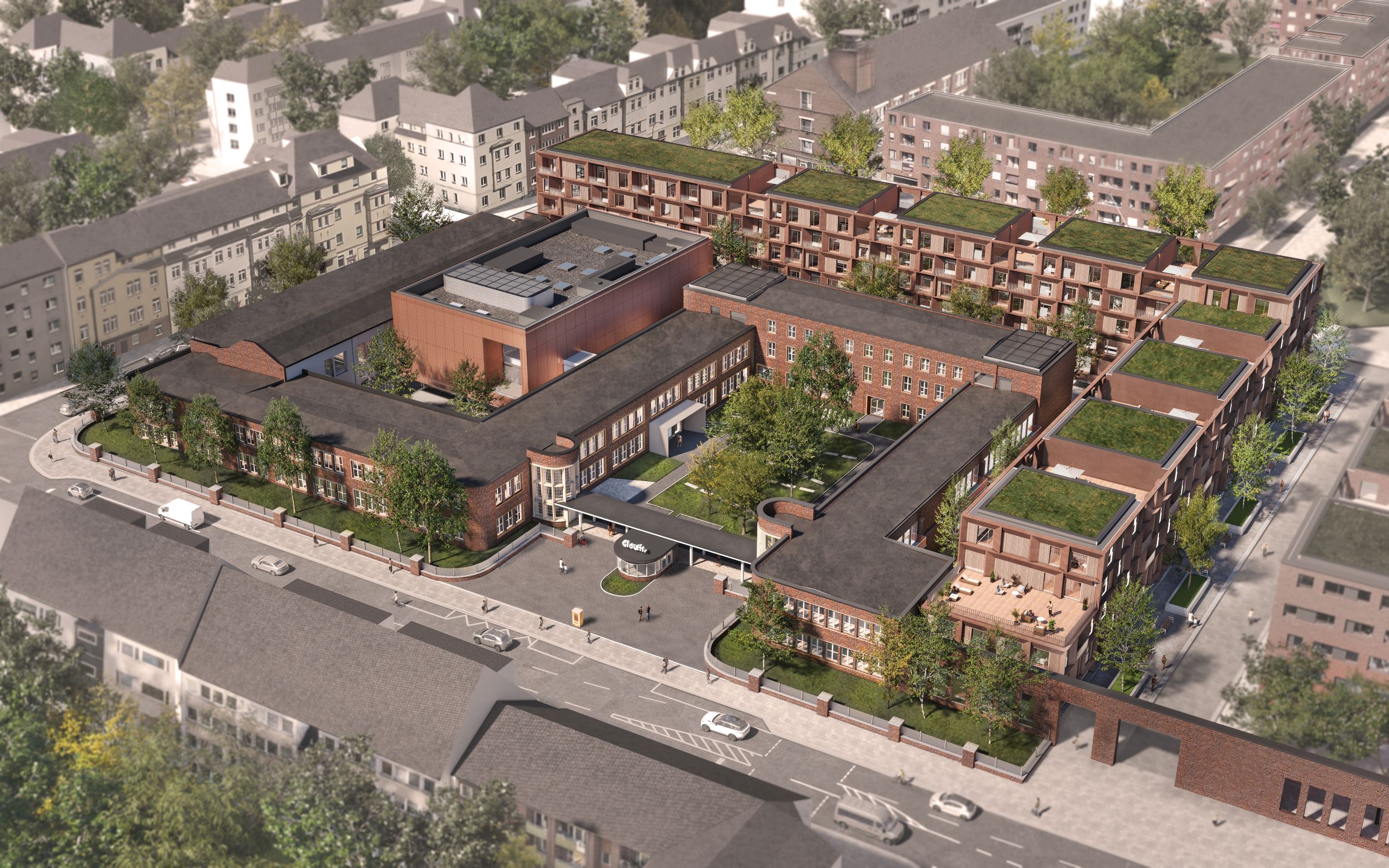
With a well thought-out sustainability approach, the project shows how climate protection and urban densification can harmonize. By continuing to use the existing structure, material resources are conserved to a considerable extent and CO₂ emissions are also avoided. Not only the supporting structure, but also intact interior surfaces such as the floor coverings on the ground floor and basement are retained.
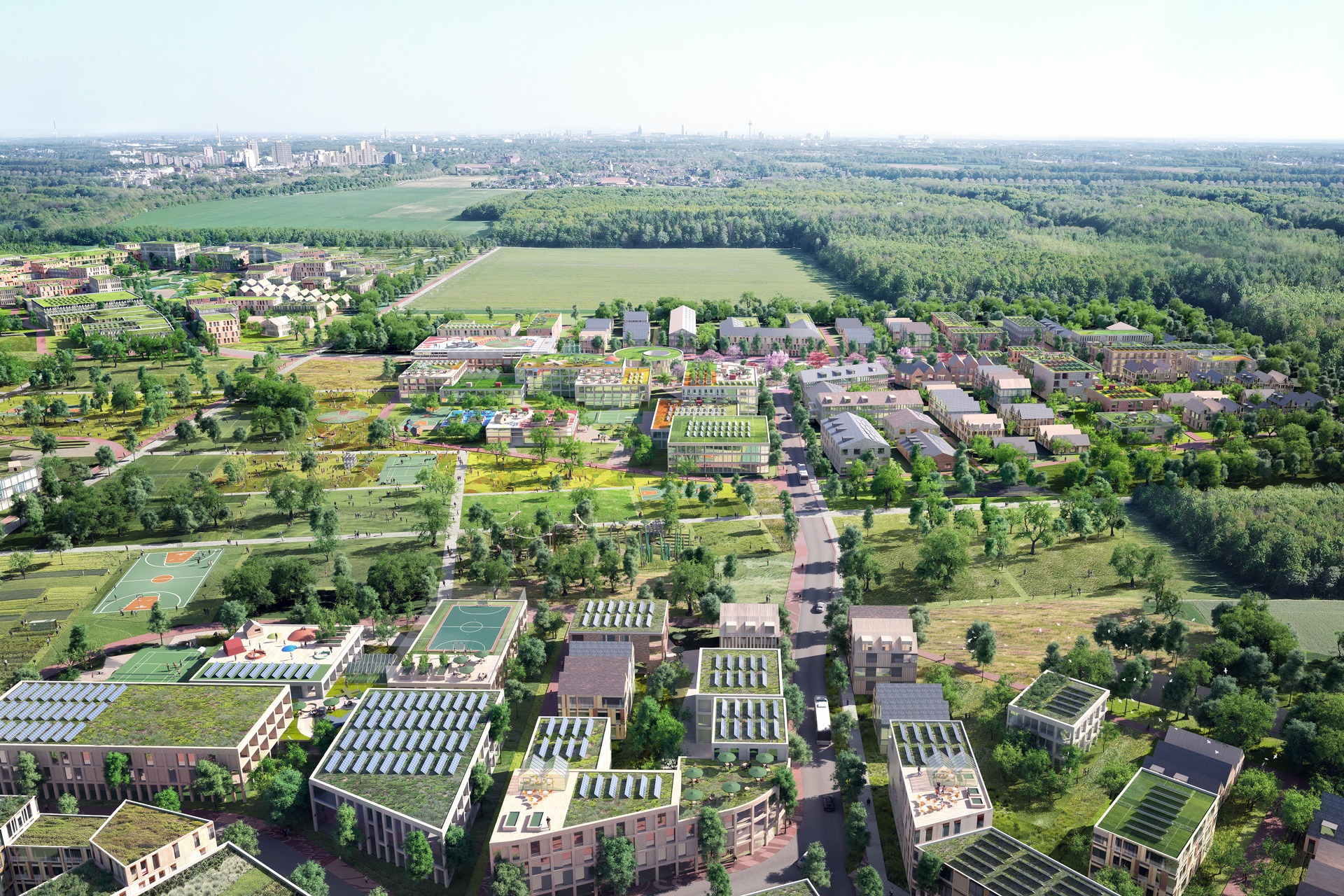
The new roof extension in timber construction is a central component of the sustainable concept. The environmentally friendly, lightweight construction material improves the statics of the building and provides additional living space without sealing any surfaces. The newly designed inner courtyard contributes to the natural lighting of all above-ground storeys and offers high-quality recreational and play areas that increase the quality of life for users.
Green facades and roofs improve the microclimate and help to bind CO₂, particulate matter and nitrogen oxides. These green elements contribute to air purification and create a pleasant environment that benefits the health and well-being of residents.
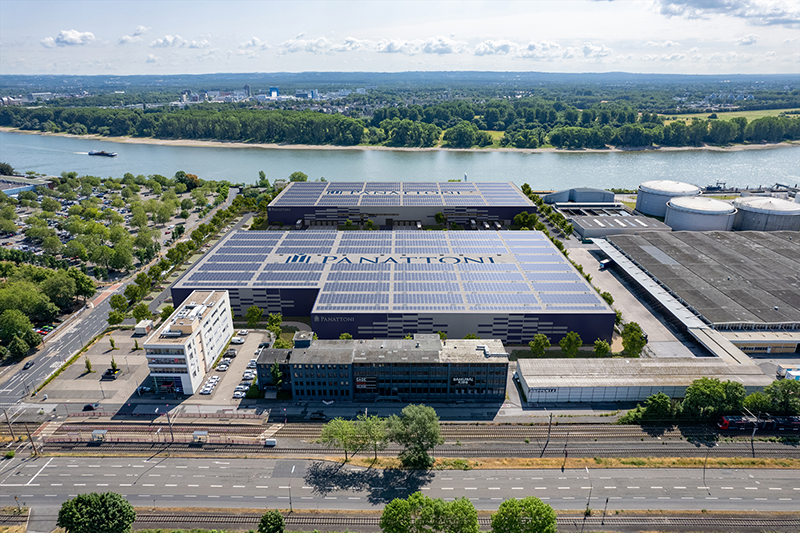
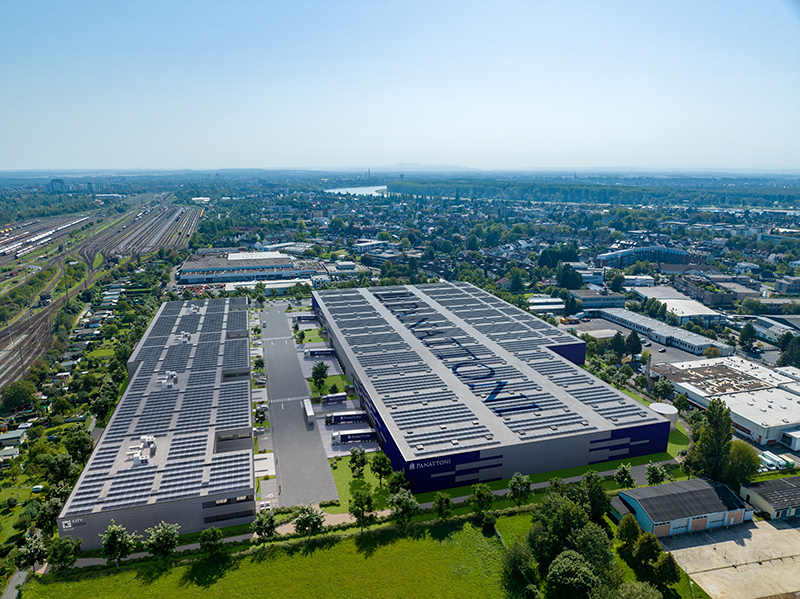
An air-to-water heat pump is used for the energy supply, which ensures efficient heating, supplemented by photovoltaic systems comprising elevated roof modules and façade-integrated elements. The cooling effect of the green roof also increases the energy generated by the photovoltaic system. This reduces greenhouse gas emissions by around 50 percent compared to an average new building, making the project an example of sustainable urban development that takes equal account of economy and ecology.